How To Build Mesa for AMD
What
copy from Wikipidia:
Mesa is an open source implementation of OpenGL, Vulkan, and other graphics API specifications. Mesa translates these specifications to vendor-specific graphics hardware drivers.
Vendor Drivers
Mesa is UMD (User mode driver), provides implementation of graphics API and shader compiler. Mesa is like a mono repository, different vendor drivers and graphics APIs are in different directories.
Gallium is a driver project in mesa, includes many backends for hardwares:
- AMD driver for GCN & Navi (radeonsi)
- Intel driver for iris (i965)
- Intel driver (i915)
- Nvidia driver (nouveau)
- Software implementation (swrast)
- OpenGL over Vulkan (zink)
- DirectX3D 12 driver (d3d12)
- OpenCL frontend (clover)
- new OpenCL frontend by rust (rusticl, 23.1)
libgl only provides APIs, and dispatch call to vendor implementation (e.g. radeonsi).
Vulkan’s driver includes:
- AMD driver (RADV)
- Intel driver (ANV)
- Nvidia driver (NVK, 23.3)
- Windows driver (dzn)
Internal Representation
NIR (NIR Internal Representation) is shader language intermediate representation in Mesa. Input is spir-v or glslang, output is vendor ISA code. NIR is used in all drivers on OpenGL 4.6.
TGSI (the Tungsten Graphics Shader Infrastructure) is used all gallium drivers, now NIR is main development ir. GLSL-to-TGSI is removed from Mesa, NIR-To-TGSI will be deprecated for native NIR drivers only.
in AMD drivers, shader compilation flows following picture (outdated, now radeonsi supports spirv to nir):
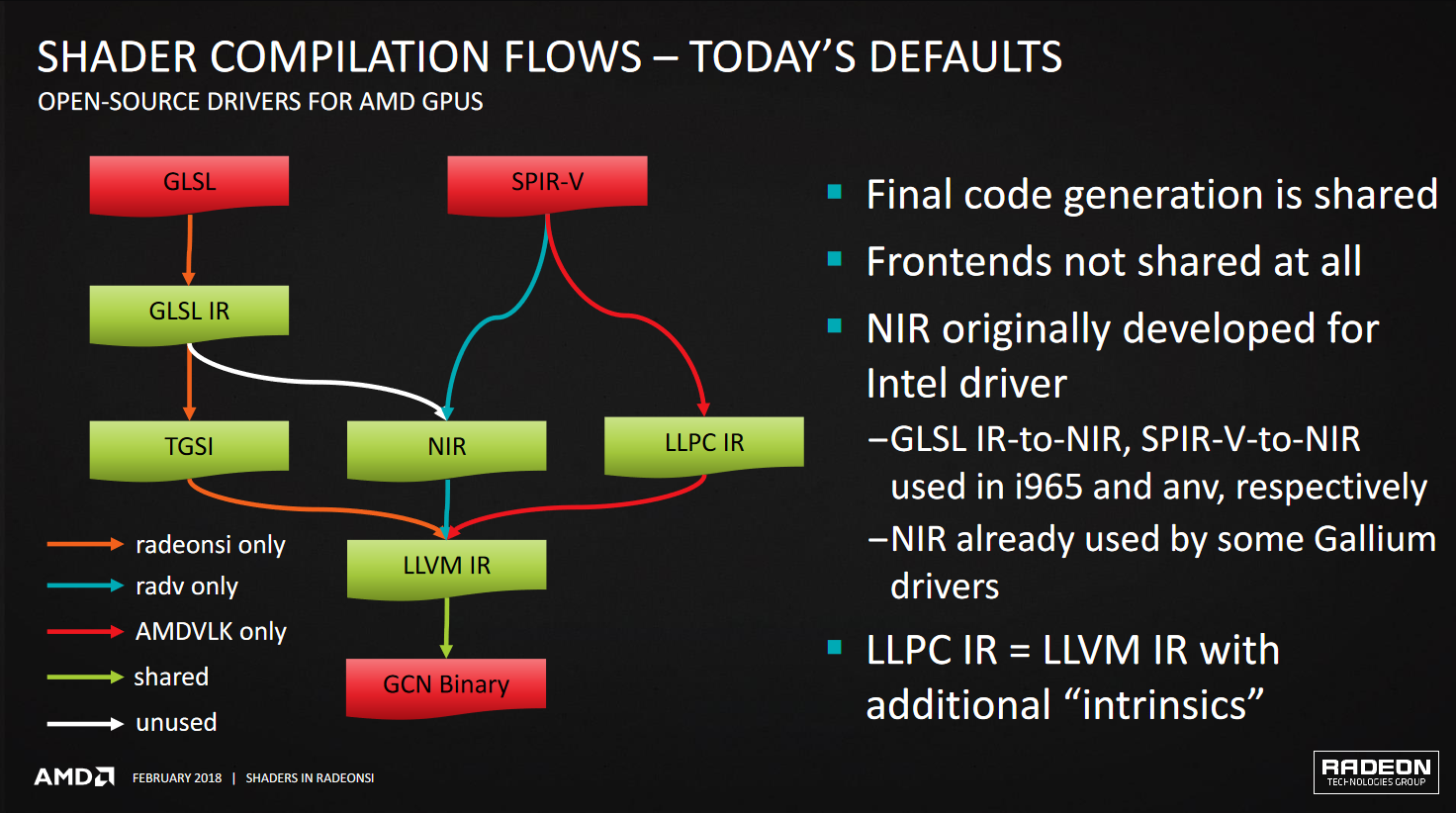
Repository
a brief summary of part of Mesa’s directory tree.
- docs - Documentation
- include - Public OpenGL header files
- src
- amd - AMD-specific sources
- addrlib - common sources for creating images
- ci - devops for RADV, RadeonSI and ACO
- common - common code between RADV, RadeonSI and ACO
- compiler - ACO shader compiler
- llvm - common code between RADV and RadeonSI for compiling shaders using LLVM
- registers - register definitions
- vulkan - RADV Vulkan implementation for AMD Southern Island and newer
- compiler - Common utility sources for different compilers
- clc - the OpenCL C language compiler
- glsl - the GLSL IR and compiler
- nir - the NIR IR and compiler
- spirv - the SPIR-V compiler
- gallium - Gallium3D source code
- auxiliary - Gallium support code
- drivers - Gallium3D device drivers
- frontends - These implement various libraries using the device drivers
- gbm - Generic Buffer Manager is a memory allocator for device buffers
- microsoft - Microsoft Graphics Stack
- clc - compile clc to dxil / nir
- compiler - the dxil and nir compiler
- spirv_to_dxil - cross spir-v to dxil
- vulkan - Microsoft vulkan driver on Windows for WSL
- vulkan - Common code for Vulkan drivers
- amd - AMD-specific sources
Build
if you want to build 32-bit mesa, please install 32-bit development packages. e.g. zlib-devel-32bit
some packages haven’t 32-bit package on openSUSE, you need to copy 64-bit
pkg-config file (.pc in /usr/lib64/pkgconfig) to /usr/lib/pkgconfig, and modify
prefix variable.
Dependencies
-
base tools
zypper install python3 python3-Mako meson ninja gcc gcc-c++ binutils-gold clang lld ccache bison flex -
minimize dependencies
zypper install zlib-devel libzstd-devel llvm-devel libexpat-devel libdrm-devel libudev-devel libelf-devel glslang-devel spirv-tools zypper install -t pattern devel_vulkan -
window manager dependencies
- X11
zypper install libX11-devel libXext-devel libxcb-devel libXfixes-devel libXxf86vm-devel libXrandr-devel libxshmfence-devel - wayland
zypper install wayland-devel wayland-protocols-devel
- X11
-
video codecs dependencies
zypper install libvdpau-devel libva-devel -
opencl dependencies
zypper install libclc libLLVMSPIRVLib-devel clang-devel zypper install rust rust-bindgen # if enable new opencl frontend -- rusticl
configuration and compilation
- common build
meson setup /path/to/mesa _build --libdir=lib64 --prefix $HOME/.local/lib/mesa \ -Dbuildtype=debug -Dosmesa=false -Dgallium-drivers=radeonsi -Dvulkan-drivers=amd - build with video codecs
meson setup /path/to/mesa _build --libdir=lib64 --prefix $HOME/.local/lib/mesa \ -Dbuildtype=debug -Dosmesa=false -Dgallium-drivers=radeonsi -Dvulkan-drivers=amd \ -Dvideo-codecs=vc1dec,h264dec,h264enc,h265dec,h265enc - build only for wayland
meson setup /path/to/mesa _build --libdir=lib64 --prefix $HOME/.local/lib/mesa \ -Dbuildtype=debug -Dosmesa=false -Dgallium-drivers=radeonsi -Dvulkan-drivers=amd \ -Dplatforms=wayland -Dglx=disabled - build with opencl frontend (clover)
meson setup /path/to/mesa _build --libdir=lib64 --prefix $HOME/.local/lib/mesa \ -Dbuildtype=debug -Dosmesa=false -Dgallium-drivers=radeonsi \ -Dgallium-opencl=icd - build with opencl frontend (rusticl)
meson setup /path/to/mesa _build --libdir=lib64 --prefix $HOME/.local/lib/mesa \ -Dbuildtype=debug -Dosmesa=false -Dgallium-drivers=radeonsi \ -Dgallium-opencl=disabled -Dgallium-rusticl=true - specifying compiler toolchain & 32-bit build
CC='ccache clang -m32' CXX='ccache clang++ -m32' LDFLAGS='-fuse-ld=lld -m32' \ meson setup /path/to/mesa _build --libdir=lib --prefix $HOME/.local/lib/mesa \ -Dbuildtype=debug -Dosmesa=false -Dgallium-drivers=radeonsi -Dvulkan-drivers=amd
compile mesa if configure successfully
meson compile -C_buildafter compilation, install mesa. that is, copy shared libraries, icd files, header files, and so on into prefix directory.
installed directory tree looks like:
prefix-dir
├── lib64
│ ├── dri
│ │ ├── kms_swrast_dri.so
│ │ ├── radeonsi_dri.so
│ │ ├── radeonsi_drv_video.so
│ │ ├── swrast_dri.so
│ │ └── zink_dri.so
│ ├── libEGL.so -> libEGL.so.1
│ ├── libEGL.so.1 -> libEGL.so.1.0.0
│ ├── libEGL.so.1.0.0
│ ├── libgbm.so -> libgbm.so.1
│ ├── libgbm.so.1 -> libgbm.so.1.0.0
│ ├── libgbm.so.1.0.0
│ ├── libglapi.so -> libglapi.so.0
│ ├── libglapi.so.0 -> libglapi.so.0.0.0
│ ├── libglapi.so.0.0.0
│ ├── libGLESv1_CM.so -> libGLESv1_CM.so.1
│ ├── libGLESv1_CM.so.1 -> libGLESv1_CM.so.1.1.0
│ ├── libGLESv1_CM.so.1.1.0
│ ├── libGLESv2.so -> libGLESv2.so.2
│ ├── libGLESv2.so.2 -> libGLESv2.so.2.0.0
│ ├── libGLESv2.so.2.0.0
│ ├── libGL.so -> libGL.so.1
│ ├── libGL.so.1 -> libGL.so.1.2.0
│ ├── libGL.so.1.2.0
│ ├── libvulkan_radeon.so
│ └── pkgconfig
│ ├── dri.pc
│ ├── egl.pc
│ ├── gbm.pc
│ ├── glesv1_cm.pc
│ ├── glesv2.pc
│ └── gl.pc
└── share
└── vulkan
└── icd.d
└── radeon_icd.x86_64.jsonUsage
OpenGL command
for 64-bit driver, running glxgears (for gl) and vkcube (for vulkan) to test that mesa is installed successfully.
# test for 64-bit OpenGL driver
MESA=$HOME/.local/lib/mesa LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$MESA/lib64:$MESA/lib \
LIBGL_DRIVERS_PATH=$MESA/lib64/dri:$MESA/lib/dri MESA_LOADER_DRIVER_OVERRIDE=radeonsi \
/usr/bin/glxgearsenvironment variable LIBGL_DRIVERS_PATH means where to find *_dri.so
library, environment variable MESA_LOADER_DRIVER_OVERRIDE means that the driver
you want to use is what. If setup the multiple gallium drivers, we can
determinate which driver is used by MESA_LOADER_DRIVER_OVERRIDE.
likes 64-bit command, test 32-bit driver following command:
# test for 32-bit OpenGL driver
MESA=$HOME/.local/lib/mesa LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$MESA/lib64:$MESA/lib \
LIBGL_DRIVERS_PATH=$MESA/lib64/dri:$MESA/lib/dri MESA_LOADER_DRIVER_OVERRIDE=radeonsi \
/usr/lib/mesa-demos/xdemos/glxgearsVulkan command
test vulkan driver
MESA=$HOME/.local/lib/mesa ICDDIR=$MESA/share/vulkan/icd.d \
VK_ICD_FILENAMES=$ICDDIR/radeon_icd.x86_64.json:$ICDDIR/radeon_icd.x86.json \
/usr/bin/vkcubeACO (_A_MD _Co_mpiler) is a new shader compiler in RADV, developed by Valve. Since mesa version 20.2, the ACO compiler is enabled by default.
for debugging, maybe we want to change the behavior of driver and shader
compiler, environment variables RADV_DEBUG and ACO_DEBUG can help us.
do various things for RADV:
- llvm: enable LLVM compiler backend
- img: Print image info
- info: show GPU-related information
- metashaders: dump internal meta shaders
- nocache: disable shaders cache
- nomemorycache: disable memory shaders cache
- nongg: disable NGG for GFX10 (navi1 & navi2)
- nonggc: disable NGG culling on GPUs where it’s enabled by default (GFX10.3+ only).
- nort: skip executing vkCmdTraceRays and ray queries (RT extensions will still be advertised)
- shaders: dump shaders
- shaderstats: dump shader statistics
- spirv: dump SPIR-V
do various things for ACO:
- perfwarn: abort on some suboptimal code generation
- force-waitcnt: force emitting waitcnt states if there is something to wait for
- force-waitdeps: force emitting waitcnt dependencies for debugging hazards on GFX10+
- novn: disable value numbering
- noopt: disable various optimizations
- nosched: disable instructions scheduling
- perfinfo: print information used to calculate some pipeline statistics
learn more in Mesa documation.
for example, debugging will disable cache and dump shaders.
MESA=$HOME/.local/lib/mesa ICDDIR=$MESA/share/vulkan/icd.d \
VK_ICD_FILENAMES=$ICDDIR/radeon_icd.x86_64.json:$ICDDIR/radeon_icd.x86.json \
RADV_DEBUG=nocache,shaders ACO_DEBUG=force-waitcnt,force-waitdeps \
/usr/bin/vkcube --c 1lucky, RGP (Radeon GPU Profiler) support vulkan on linux. we can create RGP
capture with radv in /tmp.
touch /tmp/trigger
MESA=$HOME/.local/lib/mesa ICDDIR=$MESA/share/vulkan/icd.d \
VK_ICD_FILENAMES=$ICDDIR/radeon_icd.x86_64.json:$ICDDIR/radeon_icd.x86.json \
RADV_THREAD_TRACE_PIPELINE=1 RADV_THREAD_TRACE_TRIGGER=/tmp/trigger \
/usr/bin/vkcube --c 1OpenCL command
test OpenCL
MESA=$HOME/.local/lib/mesa LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$MESA/lib64 clinfousing rusticl
MESA=$HOME/.local/lib/mesa LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$MESA/lib64 \
RUSTICL_ENABLE=radeonsi \
clinfo